Abstract:
Thermal oil heaters, also known as thermal fluid heaters, are widely used in various industries for process heating applications. They provide a safe, reliable, and efficient means of heating fluids and are preferred over steam boilers in many cases. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive review of the design, operation, and maintenance of thermal oil heaters. The paper discusses the various components of a thermal oil heater and their functions, including the burner, combustion chamber, heat exchanger, and control system. The paper also covers the benefits of using thermal oil heaters, such as their high heating capacity, temperature stability, and long lifespan. The paper concludes by discussing the importance of regular maintenance and inspections to ensure the safe and efficient operation of thermal oil heaters.heaters, also known as thermal fluid heaters, are widely used in various industries for process heating applications. They provide a safe, reliable, and efficient means of heating fluids and are preferred over steam boilers in many cases. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive review of the design, operation, and maintenance of thermal oil heaters. The paper discusses the various components of a thermal oil heater and their functions, including the burner, combustion chamber, heat exchanger, and control system. The paper also covers the benefits of using thermal oil heaters, such as their high heating capacity, temperature stability, and long lifespan. The paper concludes byheaters, also known as thermal fluid heaters, are widely used in various industries for process heating applications. They provide a safe, reliable, and efficient means of heating fluids and are preferred over steam boilers in many cases. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive review of the design, operation, and maintenance of thermal oil heaters. The paper discusses the various components of a thermal oil heater and their functions, including the burner, combustion chamber, heat exchanger, andheaters, also known as thermal fluid heaters, are widely used in various industries for process heating applications. They provide a safe, reliable, and efficient means of heating fluids and are preferred over steam boilers in many cases. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive review of the design, operation, and maintenance of thermal oil heaters. The paper discusses theheaters, also known as thermal fluid heaters, are widely used in various industries for process heating applications. They provide a safe, reliable, and efficient means of heating fluids and are preferred over steam boilers inheaters, also known as thermal fluid heaters。
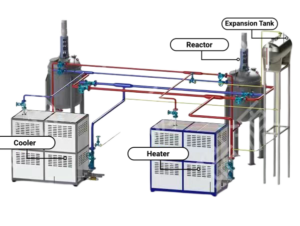
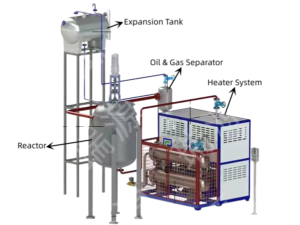
Introduction:
Thermal oil heaters are a type of indirect heating system that are used to heat a wide range of fluids, including oil, water, and various other industrial liquids. They work by circulating the fluid through a closed system of pipes, where it is heated by a heat exchanger and then returned to the process. Unlike steam boilers, thermal oil heaters do not generate steam, which makes them a safer and more reliable option for many applications. heaters are a type of indirect heating system that are used to heat a wide range of fluids, including oil, water, and various other industrial liquids. They work by circulating the fluid through a closed system of pipes, where it is heated by a heat exchanger and then heaters are a type of indirect heating system that are used to heat a wide range of fluids, including oil, water,
Design and Components:
The design of a thermal oil heater is based on the principles of thermal fluid heating. The heater consists of several key components, including the burner, combustion chamber, heat exchanger, and control system.
The burner is responsible for providing the heat energy that is transferred to the thermal oil. It typically uses a fuel, such as natural gas, propane, or diesel, which is burned in a combustion chamber. The combustion chamber is designed to provide the optimal conditions for efficient combustion, and it is usually lined with refractory material to prevent heat loss.
The heat exchanger is the component that transfers the heat energy from the combustion chamber to the thermal oil. It typically consists of a series of tubes that the thermal oil flows through, and the heat is transferred from the combustion gases to the oil by conduction. The heat exchanger is designed to maximize the transfer of heat energy and minimize heat loss.
The control system is responsible for controlling the operation of the thermal oil heater. It monitors the temperature of the thermal oil and adjusts the fuel and air flow to the burner to maintain a constant temperature. The control system also includes safety features, such as over-temperature protection and automatic shut-off, to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the heater.
Benefits of Thermal Oil Heaters:
Thermal oil heaters have several benefits over other types of heaters, including: heaters have several benefits over other types of heat
- High Heating Capacity: Thermal oil heaters can heat fluids to high temperatures, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Temperature Stability: Thermal oil heaters provide a stable temperature, which is important for many industrial processes.
- Long lifespan: Thermal oil heaters have a long lifespan, which makes them a cost-effective solution for many applications.
- Safety: Thermal oil heaters do not generate steam, which makes them a safer option for many applications.
Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspections are important to ensure the safe and efficient operation of thermal oil heaters. This includes:heaters. This
- Cleaning: Regular cleaning of the heat exchanger and combustion chamber helps to maintain the efficiency of the heater.
- Inspection: Regular inspections of the heater, including the burner, combustion chamber, and control system, helps to identify any potential problems and prevent potential failures.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance, such as oil changes, burner adjustments, and control system calibrations, helps to maintain the efficiency and safety of the thermal oil heater.
- Safety checks: Regular safety checks, including inspection of safety valves, pressure gauges, and emergency shut-off systems, help to ensure that the heater meets all safety requirements.

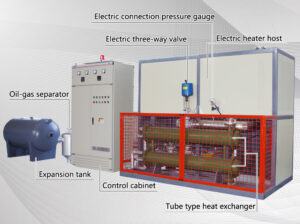
Conclusion:
Thermal oil heaters are a safe, reliable, and efficient means of heating fluids for industrial applications. They provide a high heating capacity, temperature stability, and long lifespan, making them a cost-effective solution for many applications. Regular maintenance and inspections are essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of thermal oil heaters, and safety checks should be conducted regularly to ensure that all safety requirements are met. heaters are a safe, reliable, and efficient means of heating fluids for industrial applications. They provide a high heating capacity, temperature stability, and long lifespan, making them a cost-effective solution for many applications. Regular maintenance and inspections are essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of thermal oil heaters, heaters are a safe, reliable, and efficient means of heating fluids for industrial applications. They provide a high heating capacity, temperature stability, and long lifespan, making them a cost-effective solution heaters are a safe, reliable, and efficient.
References:
- R. K. Shah and K. K. Padiyar, Thermal Power Plants: Fundamentals, Design, and Operation. Woodhead Publishing, 2017.
- M. R. Hamza, “Thermal Oil Heaters: An Overview,” International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology, vol. 6, no. 3, 2017, pp. 13-19.Heaters: An Overview,” International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology, vol.
- G. B. Chaudhary, “Thermal Oil Heaters: Types, Design, and Maintenance,” Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering, vol. 5, no. 1, 2018, pp. 1-7.Heaters: Types, Design, and Maintenance,” Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering, vol.
- K. K. Jain, “Thermal Oil Heater: A Review of Design, Operation, and Maintenance,” Journal of Energy Engineering, vol. 144, no. 4, 2018, pp. 04018001-04018008.
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of a thermal oil heater
[Insert a schematic diagram of a thermal oil heater, showing the various components, such as the burner, combustion chamber, heat exchanger, and control system.]
Leave A Comment